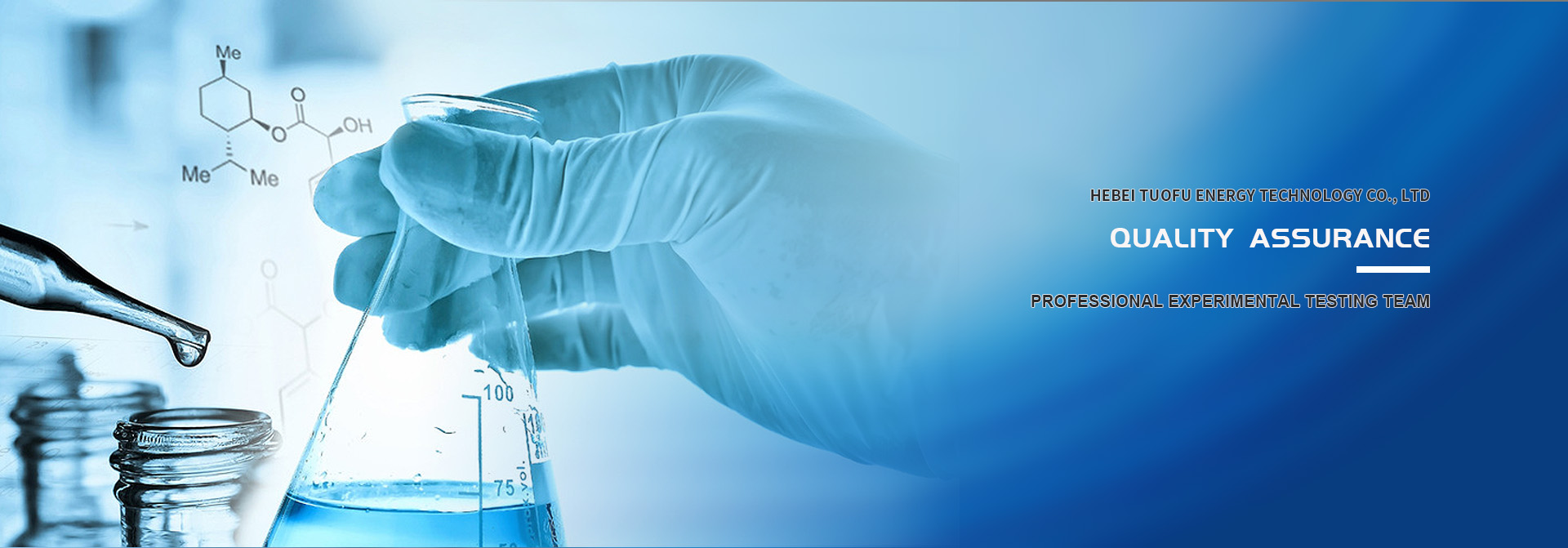
Rust inhibitor is a very polar compound, its polar group has a strong adsorption force on the metal surface, forming a tight monomolecular or multi-molecular protective layer on the metal surface, preventing the corrosive medium from contacting the metal, and acting as a rust inhibitor. to anti-rust effect. In addition, the base oil that dissolves the anti-rust agent can be adsorbed in the place where the anti-rust agent is less adsorbed, penetrates deep into the molecules of the anti-rust additive, and uses the van der Waals force to work with the additive molecule to make the adsorption film stronger; The role of oil makes the additive more firmly adsorbed on the metal surface and is not easy to detach. Oil can also form a concentrate with the additive, thereby making the adsorption film tighter. In short, these functions of base oil are beneficial to protect the adsorption molecules, maintain the thickness of the oil film, and play a certain anti-rust effect. The most commonly used corrosion inhibitors such as: barium sulfonate, calcium sulfonate, modified calcium sulfonate, amine borate, amine carboxylate


+86-0311-85123669


Customer service